Chapter 1: What is Cloud Computing?
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing: term used to describe on-demand access to IT services (e.g. network, storage, software services, etc) via public internet or WAN (wide area network) access.
The six advantages of cloud computing
- Trade capital expense for variable expense: Instead of hosting on-premises infrastructure, moving to cloud computing provides benefits (i.e. it offers a better way for paying the infrastructure)
- pay same infrastructure only as and when you consume them
- shift away from CAPEX (capital expense) to OPEX (operating expense, or variable expense)
- Benefit from massive economics of scale: Company or person has to purchase hardware/software using retail price, while AWS can purchase in bulk and then distribute to its customers using lower purchasing price.
- Stop guessing capacity
- Increase speed and agility: Cloud vendors (e.g. AWS) enable customers to launch and configure new IT resources with few mouse clicks
- Stop spending money running and maintaining data centers: maintein on-premises infrastructure have hidden costs (requires capital investment and long-term employment of professional teams)
- Go global in minutes
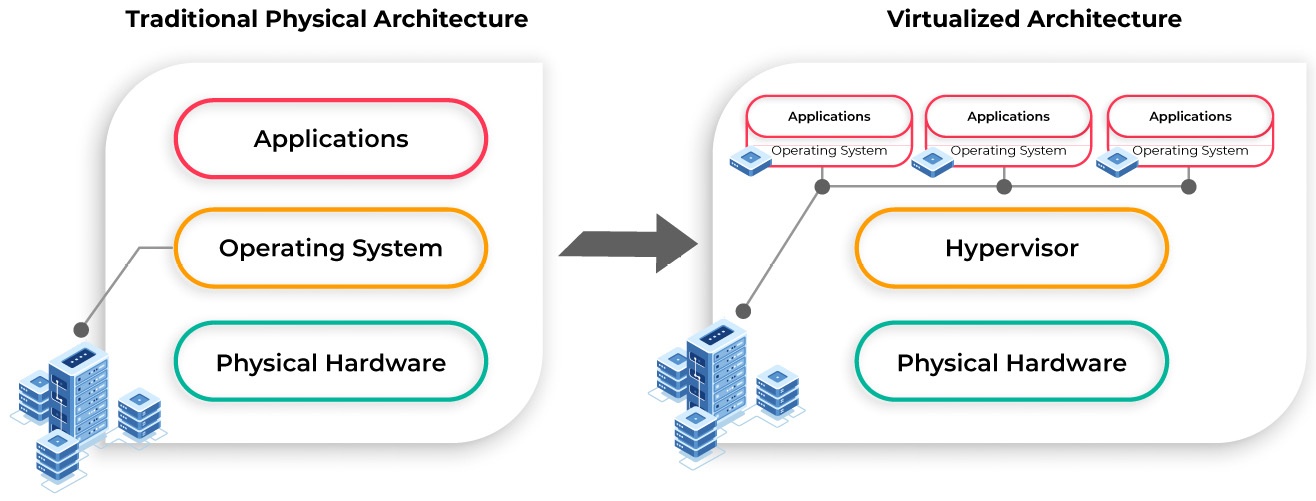
Exploring the basics of virtualization
Hardware resources are rarely consumed to their maximum capability by a single OS:
- Hardware improved significantly as shown by Moore's law
- Software become more efficiently due to advance of software architecture
Virtualization: one core tech used to enable cloud computing.
- Virtualization + Hypervisors made it possible to emulate the physical hardware components of a single physical server as multiple virtual components (i.e. Virtual Machines)
Hypervisor: a software sits between physical hardware and VMs
- Responsibility: enable OS & app (contained in VM) to access resources of physical hardware in a controlled manner.
Virtual Machines: each VM contain OS and a suite of app
Benefit of virtualization: reduce provision time of resources dramatically compare to physically provision a physical server
Virtualization vs Cloud computing
One primary service of cloud computing provider: provision virtualized infrastructure resources using a self-service management tool.
Tools offered by AWS:
- Management Console (via web browser)
- Command-line interface (CLI)
- Application programming interface (APIs)
Exploring cloud computing models
Line-Of-Businesss (LOB): apps developed by companies that need to run on web infrastructure
3 main cloud models offered by vendors
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): customer can/need configure underlying network, storage, and compute services to power their LOB apps.
- e.g. EC2, EBS, EFS, Azure VM
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): provider provision infrastructure (OS, compute, storage, network services, runtime environment) needed to deploy app. e.g. from AWS
- e.g. AWS Elastic Beanstalk, AWS OpsWorks, AWS Lambda, Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS)
- e.g. Azure Functions
- Software as a Service (SaaS): app completely hosted/managed by provider
- e.g. Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365
Understanding cloud deployment models
3 primary models of deployment:
- Public cloud
- Private cloud
- Hybrid cloud