Table of Contents
- ASP.NET MVC - Basic
- ASP.NET MVC Folder and File Structure
- Controllers in ASP.NET MVC App
- Views in ASP.NET MVC
- What are Views in ASP.NET MVC?
- Where ASP.NET MVC View Files are Stored?
- Understanding Views (Error)
- How to create/add Views in ASP.NET MVC Application?
- Models in ASP.NET MVC
- ViewData in ASP.NET MVC
- ViewBag in ASP.NET MVC
- What is ViewBag in ASP.NET MVC?
- How to Pass and Retrieve data From ViewBag in ASP.NET MVC?
- Difference and Similarities
- Strongly Typed View in ASP.NET MVC
- Creating Stronly Typed View in MVC
- Advantages of using Strongly Typed View in ASP.NET MVC Application:
- ViewModel in ASP.NET MVC
- TempData in ASP.NET MVC
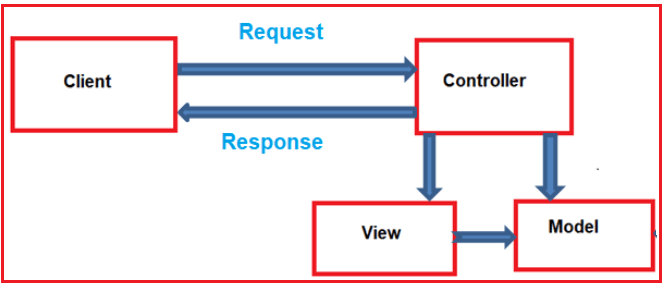
ASP.NET MVC - Basic
ASP.NET MVC Folder and File Structure
After creating ASP.NET MVC app, there is a default file system generated by .NET Framework 4.8
Summary:
- Directories:
App_Data/: contain app related data files like .mdf files, LocalDB, XML file. IIS won't serve files from this directoryApp_Start/: contain files (classes) needed to be executed at app start time (mostly configuration files). e.g. of classes:BundleConfig,FilterConfig,RouteConfig, etc.Content/: store static files. e.g. imgs, CSS, iconsControllers/: contain all controllers classesfonts/: custom font filesModels/: store class files of domain data. e.g. business logicScripts/: contain JS files. e.g. jQuery, bootstrapViews/:store.cshtmlfiles used to render HTML.- Each subdir in
Viewscorrespond to a controller - Also has a Shared folder for shared views. e.g. error, layout, etc.
- Each subdir in
- Config files created by framework when creating project:
Global.asax/store code to run at app level (explained later)Packages.config: NuGet packagesWeb.config/: store application-level configurations
Controllers in ASP.NET MVC App
Summary of Controllers:
- Parent class of Controller: A controller in MVC is a class that's inherited from
System.Web.Mvc.Controller - Function of Controller: interact with Models and Views
- Location of Controller classes: must be located in
/Controllerfolder - What it has: A controller class contains a set of public methods which are called action methods. These action methods are used to handle incoming URL.
- Naming pattern of Controller
.csfiles: In ASP.NET MVC, every controller class name must end with word "Controller". e.g. controller for the home page must beHomeController, controller for a student must beStudentController
What's a Controller in ASP.NET MVC?
- A Controller = a class with public methods (aka action methods or simple actions). These public methods are used by MVC to handle incoming HTTP requests.
How to Create a Controller in MVC?
IDE provides GUI shortcut to create controller following Adding Controller to the Project
- Location of Controllers:
- in ASP.NET MVC, controller classes are in
/Controllersfolder and inheritSystem.Web.Mvc.Controller, named asxxxController
- in ASP.NET MVC, controller classes are in
- URL mapping in ASP.NET MVC:
http://localhost:xxxx/Home/Indexmap to classHomeController->Index()method- This mapping is defined in
RegisterRouters()method ofRouteConfigclass inApp_Startfolder (for app initialization) - Default route for HomeController (i.e.
Home/Indexpage) shown below
routes.MapRoute(
name: "Default", // Default Route
url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}", // URL Pattern
defaults: new {
controller = "Home", // Contoller for the mapped page
action = "Index", // Action method within controller
id = UrlParameter.Optional // id within page, currently it's optional
}
);
Default Controller class is shown as below
namespace FirstMVCDemo.Controllers
{
public class HomeController : Controller
{
// GET: Home
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
}
}
Which will create problem when running, as View() is not defined. So to fix the problem, we can just the public method to return string
e.g.
public string Index()
{
return "Hello MVC5 Application";
}
Also we can parse args to controller:
- URL can parse args by
/10?name=Jamesfrom URL into controller method - method can use
Request.QueryStringto retrieve string parameter
Parse string parameter method 1:
public string Index(string id, string name)
{
return "The value of Id = " + id + " and Name = " + name;
}
Parse string paramter method 2:
public string Index(string id, string name)
{
return "Id = " + id + " ,Name = " + Request.QueryString["name"];
}
To see them, enter URL http://localhost:xxxx/Home/Index/10?name=James
Views in ASP.NET MVC
What are Views in ASP.NET MVC?
Views in ASP.NET MVC = HTML templates embedded with Razor syntax. It generate/render HTML content to send to client
Where ASP.NET MVC View Files are Stored?
- Views files in ASP.NET MVC have
.cshtmlextention. (Only when we use C#) - Within
/Viewsfolder, each controller has a controller-specific subdirectory to store controller-specific.cshtmlviews. - View file name and controller action name should be the same
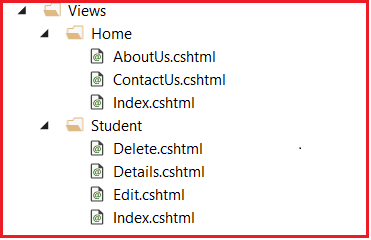
e.g. Views Folder Structure
ASP.NET MVC app has HomeController & StudentController classes, where
HomeControllerhas action methodsAboutUs(),ContactUs()andIndex()StudentControllerhas action methodsIndex(),Details(),Edit()andDelete()
Views are created in following structure
Understanding Views (Error)
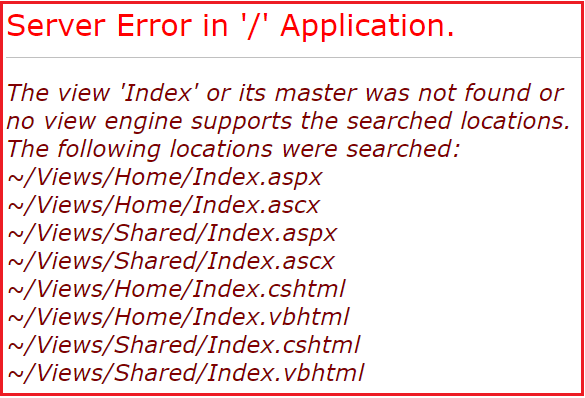
If View is not created (correctly), following message will show
Understanding the error message: When Home Controller return a view from the index action method, MVC Framework perform following search:
- Look for a file with name
Index.aspxorIndex.ascxin/Views//Homeor/Views/Sharedirectory - If not found, it search a view file
Index.cshtmlorIndex.vbhtml(for VisualBasic) within/Views/Homeor/Views/Shareddirectory
How to create/add Views in ASP.NET MVC Application?
In VS2019
- right click method (e.g.
Index()) -> Add View - Modify views by changing html content
Models in ASP.NET MVC
Summary of topic:
- What are the Models in ASP.NET MVC?
- How to create and user Models in MVC
What are the Models in ASP.NET MVC?
Models is used to manage domain data
- contain classes that represent business data
- contain classes with logic to manage business data
Location model:
- (Good practice) within Models folder of MVC
How to create & user Models in MVC
- Create
Employee.csin/Models, which has data structure that represent Employee - Create
EmployeeBusinessLayer.csin/Models, which contains business logic to manage employee data (e.g. CRUD operation) - Modify
HomeController.csto use these
e.g. Employee.cs
namespace FirstMVCDemo.Models
{
public class Employee
{
public int EmployeeId { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Address { get; set; }
public string City { get; set; }
public string Gender { get; set; }
public decimal Salary { get; set; }
}
}
e.g. EmployeeBusinessLayer.cs
namespace FirstMVCDemo.Models
{
public class EmployeeBusinessLayer
{
public Employee GetEmployeeDetails(int EmployeeId)
{
//Here we hardcoded the data
//later we will discuss how to retrieve
//the data from a database
Employee employee = new Employee()
{
EmployeeId = EmployeeId,
Name = "Pranaya",
Gender = "Male",
City = "Mumbai",
Salary = 1000,
Address = "Andheri"
};
return employee;
}
}
}
Next: learn how to pass data from controller (after extract data from Model) to view using ViewData
ViewData in ASP.NET MVC
Summary of topic:
- What is ViewData in ASP.NET MVC?
- How to Pass and Retrieve data From ViewData in ASP.NET MVC?
- Example of ViewData in ASP.NET MVC.
In ASP.NET MVC app, we can pass model data from a controller to a view in many ways:
- ViewBag (introduced here)
- ViewData
- TempData
- Session or Application State varaible from traditional Web Forms
What is ViewData in ASP.NET MVC?
ViewData = a mechanism to pass data from a controller action method to a view (Uni-directional).
- Internally It's a dictionary preoperty of
ControllerBaseclass (it's the base class ofControllerclass) - ViewData is a Dictionary type (
ViewDataDictionaryactually), whereas ViewBag is of dynamic type - As a dictionary type, it contains key-value pairs where each key must be a string. e.g.
ViewData["Name"]
using System.Web.Routing;
namespace System.Web.Mvc
{
//
// Summary:
// Represents the base class for all MVC controllers.
public abstract class ControllerBase : IController
{
//
// Summary:
// Initializes a new instance of the System.Web.Mvc.ControllerBase class.
protected ControllerBase();
public ControllerContext ControllerContext { get; set; }
public TempDataDictionary TempData { get; set; }
public bool ValidateRequest { get; set; }
public IValueProvider ValueProvider { get; set; }
//
// Summary:
// Gets the dynamic view data dictionary.
//
// Returns:
// The dynamic view data dictionary.
public dynamic ViewBag { get; }
//
// Summary:
// Gets or sets the dictionary for view data.
//
// Returns:
// The dictionary for the view data.
public ViewDataDictionary ViewData { get; set; }
protected virtual void Execute(RequestContext requestContext);
protected abstract void ExecuteCore();
protected virtual void Initialize(RequestContext requestContext);
}
}
How to Pass and Retrieve data From ViewData in ASP.NET MVC?
i.e. "How to transfer data from controller to view using ViewData"
As data are stored as an object (like JSON object) in ViewData, so retrieving data from ViewData require type casting.
- ViewData in MVC with String Type:
- Pass/Store data in Controller:
ViewData["Header"] = "Employee Details - Retreive data in View:
@ViewData["Header"](No type casting is required for string object)
- Pass/Store data in Controller:
- ViewData in MVC with Complex Type:
- Pass/Store data in Controller:
ViewData["Employee"] = employee - Retreive data in View:
- Pass/Store data in Controller:
@{
var employee = ViewData["Employee"] as FirstMVCDemo.Models.Employee;
}
Some Note about ViewData:
- ViewData in MVC is resolved dynamically at runtime. Hence, no compileer-time error checking (e.g. miss-spell key names)
e.g. from tutorialsteacher
ViewData in Action method
public ActionResult Index()
{
IList<Student> studentList = new List<Student>();
studentList.Add(new Student(){ StudentName = "Bill" });
studentList.Add(new Student(){ StudentName = "Steve" });
studentList.Add(new Student(){ StudentName = "Ram" });
ViewData["students"] = studentList;
return View();
}
Access ViewData in Razor View
<ul>
@foreach (var std in ViewData["students"] as IList<Student>)
{
<li>
@std.StudentName
</li>
}
</ul>
ViewBag in ASP.NET MVC
Topics:
- What is ViewBag in ASP.NET MVC?
- How to Pass and Retreive data from ViewBag in ASP.NET MVC?
- Example of ViewBag in MVC
- What are Difference and Similarities btw ViewData and ViewBag in ASP.NET MVC?
What is ViewBag in ASP.NET MVC?
As shown before, ViewBag is a dynamic property of Controller base class. It can transfer data from a controller action method to view
[Dynamic]
public dynamic ViewBag { get; }
How to Pass and Retrieve data From ViewBag in ASP.NET MVC?
- ViewData in MVC with String Type:
- Pass/Store data in Controller:
ViewData.Header = "Employee Details - Retreive data in View:
@ViewData.Header(No type casting is required for string object)
- Pass/Store data in Controller:
- ViewData in MVC with Complex Type:
- Pass/Store data in Controller:
ViewBag.Employee = employee; - Retreive data in View
- Advantage: No need to require typecasting while accessing data from a ViewBag
- Pass/Store data in Controller:
@{
var employee = ViewData.Employee as FirstMVCDemo.Models.Employee;
}
Note: ViewBag is a dynamic property that also resolved at runtime, so no compile-time error checking.
Difference and Similarities
Similarity:
- Both ViewData, ViewBag can be used to pass data from a Controller to a View.
- Both are used to create loosely typed views
- Both are resolved at runtime, no compiler-time error generated if mis-spell keynames or property name
Differences:
- ViewData is a dictionary object, while ViewBag is a dynamic property
- ViewData store data using key string, while ViewBag use dynamic properties
- ViewData require typecasting for complex data, and also need check for null values to avoid exception, while ViewBag does not need
Best & Preferred way to pass data from Controller to View is Strongly Typed model, introduced next topic
Strongly Typed View in ASP.NET MVC
In MVC if pass data from a Controller to a View using ViewBag, TempData, or ViewData, the view becomes a loosely typed view.
Advantage of using strongly typed views:
- Intellisense
- Compile-time error checking
Creating Stronly Typed View in MVC
- Q: How To create a strongly typed view in ASP.NET MVC app?
- A: pass the model object as a parameter to
View()extension method.
Controller base class provide 4 overloaded versions of View() extension method
protected internal ViewResult View(object model);
protected internal virtual ViewResult View (IView view, object model);
protected internal ViewResult View(string viewName, object model);
protected internal virtual ViewResult View(string viewName, string masterName, object model);
In Controller
Step 1. Pass object as parameter to View extension method
using FirstMVCDemo.Models;
using System.Web.Mvc;
namespace FirstMVCDemo.Controllers
{
public class HomeController : Controller
{
public ActionResult Index()
{
EmployeeBusinessLayer employeeBL = new EmployeeBusinessLayer();
Employee employee = employeeBL.GetEmployeeDetails(101);
ViewBag.Header = "Employee Details";
return View(employee); // pass object as parameter
}
}
}
In View
Step 1. specify model type within the view by inserting @model FirstMVCDDemo.Models.Employee (lowercase m) before <!DOCTYPE html>
Step 2. Access model properties by using @Model (uppercase M), like <td>@Model.EmployeeId</td>
Advantages of using Strongly Typed View in ASP.NET MVC Application:
Advantage of strongly typed view in ASP.NET MVC app:
- Strongly Typed View in ASP.NET MVC provides compile-time error checking as well as intelligence support.
- Mis-spell property name will be spotted at compile time
ViewModel in ASP.NET MVC
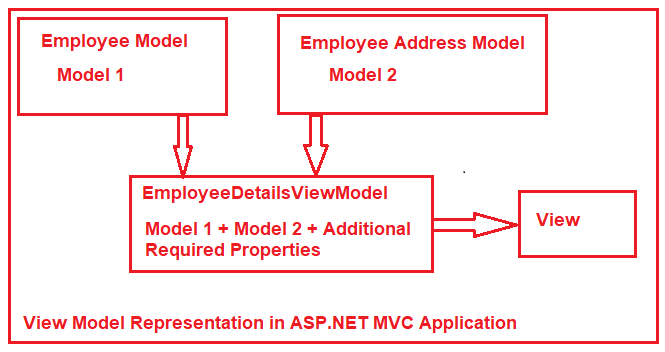
- A view may require multiple models, hence ViewModel is utilized.
- A ViewModel in ASP.NET MVC app = a model which contains more than one model data required for a particular view.
- This model is specific to a view only, hence called
ViewModel
Understanding ViewModel in ASP.NET MVC
e.g. ViewModel design
Steps to create ASP.NET MVC:
- Create models within
/Modelsdirectory. e.g.Address.cs&Employee.cs - Create a viewmodel for containing models. e.g.
EmployeeDetailsViewModel.csthat used to contain Employee and their address - Create a employee controller for using model & viewmodel, and pass ViewModel to view
- Use ViewModel like strongly typed view in the view.
TempData in ASP.NET MVC
Why do we need TempData in ASP.NET MVC App?
Limits of ViewData, ViewBag, ViewModel:
- ViewData & ViewBag: limited to onnly one HTTP request (e.g. if redirection occur, their value become null and lose data)
- ViewModel: cannot used to pass data from one controller to another.
Where to use TempData:
- Need to pass data from one HTTP Request to another.
- Need to pass data from one controller to another
What is TempData in MVC?
TempData in ASP.NET MVC is the one of mechanism used to pass small amount of temporary data:
- From 1 controller to its view (from
A->controllertoA->view) - From 1 action method to another action method within same controller (from
A->controller->method1toA->controller->method2) - From 1 controller action method to a action method in another controller (from
A->controller->methodtoB->controller->method)
Find declaration of TempData from metadata
namespace System.Web.Mvc
{
//
// Summary:
// Represents the base class for all MVC controllers.
public abstract class ControllerBase : IController
{
//
// Summary:
// Initializes a new instance of the System.Web.Mvc.ControllerBase class.
protected ControllerBase();
// ...
//
// Summary:
// Gets or sets the dictionary for temporary data.
//
// Returns:
// The dictionary for temporary data.
public TempDataDictionary TempData { get; set; }
//...
}
}
Find declaration of class TempDataDictionary in System.Web.Mvc.TempDataDictionary
public class TempDataDictionary :
IDictionary<string, object>,
ICollection<KeyValuePair<string, object>>,
IEnumerable<KeyValuePair<string, object>>,
IEnumerable
As TempDataDictionary implement IDictionary interface, in MVC TempData is a dictionary object
It store data in key-value pairs:
- Each key is a string
- Each value is stored as object type
How to Pass and Retrieve data From TempData in ASP.NET MVC:
As value are stored as object, it must be casted when retreive
- To Store data in TempData:
TempData["YourDataKey"] = "SomeDataValue"; - To retreive data from TempData:
string strData = TempData["YourDataKey"].ToString();type cast using string
e.g. pass and retreive data using TempData across action methods. However, data are not persistent
namespace FirstMVCDemo.Controllers
{
public class EmployeeController : Controller
{
public ActionResult Method1()
{
TempData["Name"] = "Pranaya";
TempData["Age"] = 30;
return View();
}
public ActionResult Method2()
{
string Name;
int Age;
if (TempData.ContainsKey("Name"))
Name = TempData["Name"].ToString();
if (TempData.ContainsKey("Age"))
Age = int.Parse(TempData["Age"].ToString());
// do something with userName or userAge here
return View();
}
public ActionResult Method3()
{
string Name;
int Age;
if (TempData.ContainsKey("Name"))
Name = TempData["Name"].ToString();
if (TempData.ContainsKey("Age"))
Age = int.Parse(TempData["Age"].ToString());
// do something with userName or userAge here
return View();
}
}
}
Activate all action methods 1 by 1 via visiting URLs one after another:
- 1st Request:
http://localhost:xxxxx/Employee/Method1 - 2nd Request:
http://localhost:xxxxx/Employee/Method2 - 3rd Request:
http://localhost:xxxxx/Employee/Method3
- We cannot access TempData in method3, as TempData will be cleared out after 2nd request.
How to retain TempData values in the consecutive request?
- Call
TempData.Keep()after retreive data
namespace FirstMVCDemo.Controllers
{
public class EmployeeController : Controller
{
public ActionResult Method1()
{
TempData["Name"] = "Pranaya";
TempData["Age"] = 30;
return View();
}
public ActionResult Method2()
{
string Name;
int Age;
if (TempData.ContainsKey("Name"))
Name = TempData["Name"].ToString();
if (TempData.ContainsKey("Age"))
Age = int.Parse(TempData["Age"].ToString());
TempData.Keep();
// do something with userName or userAge here
return View();
}
public ActionResult Method3()
{
string Name;
int Age;
if (TempData.ContainsKey("Name"))
Name = TempData["Name"].ToString();
if (TempData.ContainsKey("Age"))
Age = int.Parse(TempData["Age"].ToString());
// do something with userName or userAge here
return View();
}
}
}